by Caitlin Ennis, Acupuncturist
According to Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) theory, the first line of defence in our body is “Wei Qi”. This is a type of energy that sits just under our skin and is responsible for regulating sweating, the opening and closing of our pores and the strength of our immune system – you can think of wei qi like a protective barrier that covers the skin and helps our body fight disease.
This system is dependent on the overall function of our lungs, if our lungs are suppressed which tends to happen as we enter the colder months, our protective defence becomes impaired making our body susceptible to pathogenic invasions such as viruses and bacteria.
How can Acupuncture help?
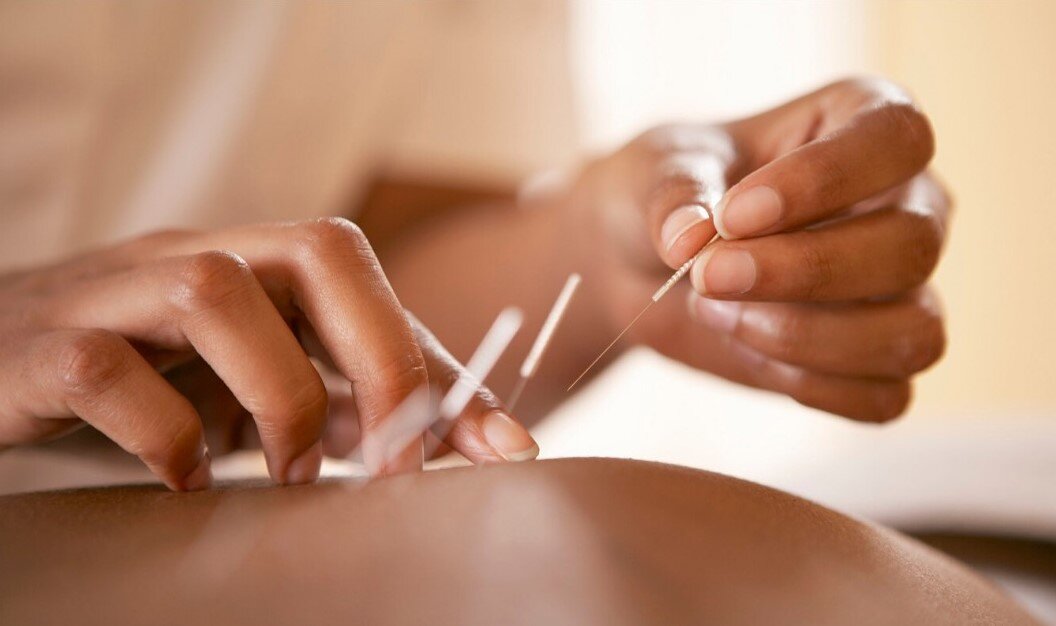
Acupuncture has been shown to help improve immunity by regulating energetic imbalances within the body. By using microfine needles, particular acupuncture points are stimulated to create a signal within the body that can stabilise neurological and hormonal imbalances. This change enables the body to function optimally and return to good health.
What is the research saying?
Scientific Research highlights acupuncture point Stomach 36 (Zusanli) for its direct influence over the immune system and powerful therapeutic action. Current research carried out by Chen et al. In 2017 showed that Stomach 36 can enhance immune cytokines and splenic CD4 + T cells. These cells are known as “helper cells” and protect the body against microbes such as viruses and bacteria. The functions of the CD4+ T cell are diverse, such as the activation of immune cells, direct cytotoxic effects, and immunoregulation.
References:
Chen, L., Xu, A., Yin, N., Zhao, M., Wang, Z., & Chen, T. et al. (2017). Enhancement of immune cytokines and splenic CD4+ T cells by electroacupuncture at ST36 acupoint of SD rats. PLOS ONE, 12(4), e0175568. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175568
*This blog features the views of the writer and is for educational purposes only. The content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your doctor or other qualified health practitioners before acting on information on this article.