UNLOCKING HAPPINESS AND WELL-BEING: THE BENEFITS OF 5-HTP AND SEROTONIN
with Reine DuBois
Serotonin, often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, plays a crucial role in maintaining our mental and physical well-being. 5-HTP (5 Hydroxytryptophan), a precursor to serotonin, has gained attention for its importance in our daily lives.
FIVE ROLES OF SEROTONIN
Serotonin, a neurotransmitter in the brain and throughout the body, plays various roles, including:
- Mood Regulation: Serotonin is often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter. It helps regulate mood, emotions, and contributes to feelings of happiness and well-being.
- Sleep Regulation:Serotonin plays a role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. It helps with the production of melatonin, a hormone that controls sleep patterns.
- Appetite Control: Serotonin is involved in appetite and satiety regulation. It can influence feelings of fullness and curb overeating.
- Cognitive Function:Serotonin is important for cognitive functions such as memory, learning, and decision-making.
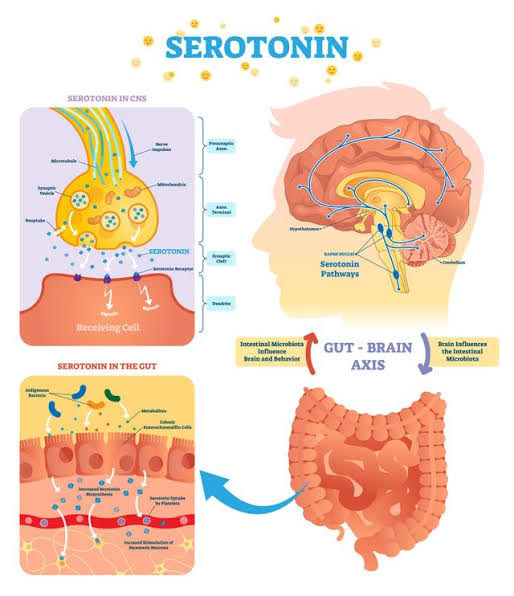
- Gastrointestinal Function: A significant portion of serotonin is found in the gut, where it helps regulate gastrointestinal motility and secretion. These are just a few of the many roles that serotonin plays in the body, and its functions are complex and interconnected with various physiological processes.
How does 5-HTP get converted to Serotonin?
5-HTP (5-Hydroxytryptophan) is a naturally occurring amino acid that’s conveyed from tryptophan. Here’s how the conversion from 5-HTP to serotonin typically occurs:
- Dietary Intake: tryptophan can be obtained from certain foods, such as turkey, chicken, and some plant sources such as cashews & chocolate. It can also be taken as a dietary supplement.
- Absorption: After ingestion of tryptophan and with the presence of the bifidobacterium, 5-HTP is converted absorbed into the bloodstream from the digestive tract.
- Penetration of the Blood-Brain Barrier:5-HTP has the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, which is a protective barrier that separates the bloodstream from the brain. This is a crucial step because serotonin primarily functions in the brain.
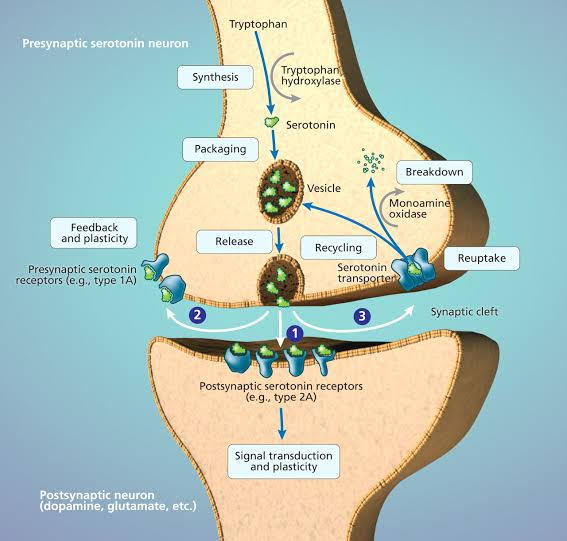
- Conversion to Serotonin: Once 5-HTP reaches the brain, it is converted into serotonin through a series of enzymatic reactions. The rate-limiting enzyme in this process is called aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC).
- Serotonin Function: Serotonin, now produced in the brain, goes on to serve its various roles in mood regulation, sleep, appetite control, and other physiological functions. It’s worth noting that the conversion of 5-HTP to serotonin is tightly regulated by the body, and the availability of cofactors like vitamin B6 & magnesium are essential for this process.
What interferes with the production of 5htp to Serotonin?
Several factors can interfere with the production of serotonin from 5-HTP in the body. These include:
- Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies: The conversion of 5-HTP to serotonin relies on the availability of cofactors, such as vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) and magnesium. Vit D has recently been found to be very important in this conversation. A deficiency in these nutrients can hinder the conversion process.
- Enzyme Dysfunction: The enzymatic reactions responsible for converting 5-HTP to serotonin can be influenced by genetic factors or enzyme deficiencies. Any disruption in these enzymes can affect serotonin synthesis.
- Diet and Nutritional Factors:A diet lacking in essential amino acids, particularly tryptophan (from which 5-HTP is derived), can limit the availability of 5-HTP for conversion to serotonin.
- Stress and Cortisol:Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels can reduce the activity of enzymes involved in serotonin synthesis, thereby decreasing serotonin production.
- Medications and Substances: Certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which are used to treat depression and anxiety, can alter serotonin levels. Additionally, substances like alcohol and recreational drugs like MDMA may disrupt serotonin balance.
- Medical Conditions: Various medical conditions, such as metabolic disorders or autoimmune diseases, can interfere with the body’s ability to convert 5-HTP to serotonin.
- Gut Health: Since a significant portion of serotonin is produced in the gut, disruptions in gut health, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammation, can impact serotonin synthesis.
It’s important to note that serotonin synthesis is a complex process, and individual factors can vary.
If you suspect issues with serotonin production or have concerns about your mood or well-being, it’s advisable to consult with a clinical nutritionist or naturopathic healthcare professional who can conduct a thorough evaluation and provide appropriate guidance and treatment options.
There are many nutrient-drug interactions with 5HTP, it’s essential this powerful amino acid is well prescribed.

Reine DuBois is an Integrative Naturopath and Clinical Director at The Health Lodge. As an Integrative Naturopath, Reine possesses an exceptional capacity to see and understand the intricacies of the human system. She is well-known for uncovering complex health conditions and coordinating treatments for chronic health issues.
To learn more about Reine and her offerings, click here
Or book online here