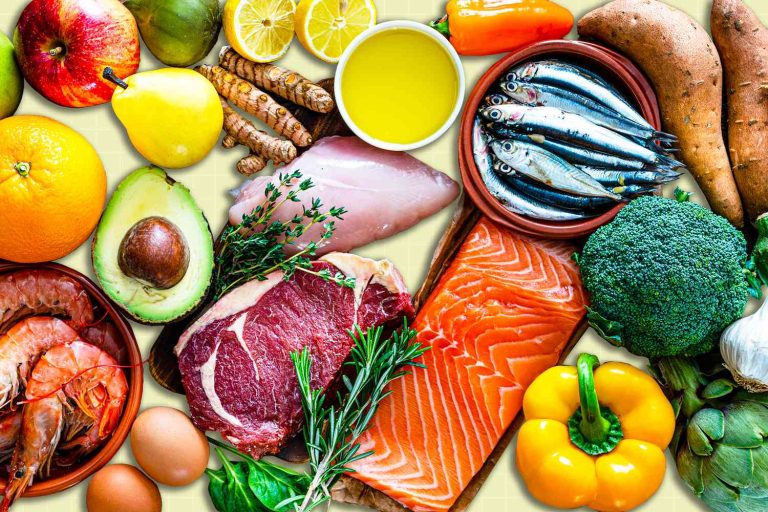
NOURISHING THE BODY, CALMING THE IMMUNE STORM: A DEEP DIVE INTO THE THERAPEUTIC POTENTIAL OF THE AIP DIET FOR AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
with Jessie Johns
Autoimmune diseases, a diverse group of conditions where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells, can be challenging for both practitioners and patients to manage. When navigating the complexities of managing these many conditions, the Autoimmune Protocol (AIP) diet emerges as a beacon of hope. In recent years, the AIP diet has gained attention as a therapeutic approach for individuals facing these complex disorders. This article aims to shed light on the benefits of the AIP diet, presenting a detailed outline of its key aspects, nutritional focusses, and supportive evidence of clinical outcomes.
Understanding the Autoimmune Protocol (AIP) Diet:
The Autoimmune Protocol (AIP) diet is a systematic approach that prioritizes the removal of potential inflammatory triggers while fostering a healing environment within the body. The diet is structured in two main phases:
Elimination Phase:
- The foundational stage of the AIP diet involves the removal of foods known to contribute to inflammation. This includes grains, legumes, dairy, processed sugars, eggs, nuts, and nightshade vegetables.
- The focus shifts towards nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory foods, such as a variety of colourful fruits and vegetables, lean and nourishing cuts of meat, fatty fish, and healthy fats like avocado and olive oil.
Reintroduction Phase:
- Following a period of strict elimination, the reintroduction phase allows individuals to systematically reintroduce excluded foods to identify specific triggers for their autoimmune symptoms.
- This personalised approach ensures that the AIP diet can be tailored to each person’s tolerance levels and nutritional needs.

Exploring the Nutritional Landscape of the AIP Diet:
Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouses:
- Turmeric and ginger, both prominent in the AIP diet, boast potent anti-inflammatory properties. The compound curcumin in turmeric has been extensively studied for its role in modulating the immune response (Sharma et al., 2017).
Bone Broth and Collagen:
- A cornerstone of the AIP diet, bone broth, and collagen support gut health and repair. Studies indicate that collagen supplementation can enhance gut barrier function, offering therapeutic potential for autoimmune conditions (Zhu et al., 2019).
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
- Fatty fish, a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, is a staple in the AIP diet. Research suggests that omega-3s play a crucial role in reducing inflammation and supporting overall immune health (Calder, 2015).
Probiotics from Fermented Foods:
- Fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi introduce beneficial probiotics, contributing to a balanced and diverse gut microbiome. A healthy gut microbiome is increasingly recognized as a key player in autoimmune disease management (Vighi et al., 2008).
Evidential Support for the AIP Diet:
Inflammatory Marker Reduction:
- Studies by Konijeti et al. (2017) demonstrate a significant reduction in inflammatory markers among participants adhering to the AIP diet, indicating its potential to quell systemic inflammation.
Gut Microbiome Modulation:
- Halmos et al. (2019) showcase the AIP diet’s positive impact on gut health, emphasizing the vital role of a balanced microbiome in immune system modulation and regulation.
Immune System Modulation:
- The AIP diet’s focus on nutrient-dense foods support immune system regulation, as highlighted in studies by Konijeti et al. (2017) and Taltavull et al. (2020).
Symptom Management and Quality of Life:
- Chrousos (2015) highlights improvements in fatigue, joint pain, and skin conditions among individuals following the AIP diet, contributing to an enhanced quality of life.
The Autoimmune Protocol (AIP) diet stands as a holistic and promising approach to managing autoimmune diseases. By addressing inflammation, supporting gut health, and modulating the immune system, the AIP diet offers a multifaceted strategy for practitioners and patients alike. It provides an opportunity to understand each unique body and its intricate immune triggers, creating an individualized approach to treatment. The AIP diet and its therapeutic outcomes highlight just how important food and nutrients are when supporting and modulating the immune system, especially for those looking to foster optimal health when grappling with autoimmune disease.
References:
Sharma, S., Chopra, K., & Kulkarni, S. K. (2017). Agomelatine attenuates LPS-induced behavioral deficits, biochemical and neurochemical abnormalities in mice. Life Sciences, 174, 41-51.
Zhu, C. F., Li, G. Z., Peng, H. B., Zhang, F., Chen, Y., & Li, Y. (2019). Treatment with marine collagen peptides modulates glucose and lipid metabolism in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 44(6), 631-637.
Calder, P. C. (2015). Marine omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Effects, mechanisms, and clinical relevance. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 1851(4), 469-484.
Vighi, G., Marcucci, F., Sensi, L., Di Cara, G., & Frati, F. (2008). Allergy and the gastrointestinal system. Clinical & Experimental Immunology, 153(Suppl 1), 3–6

Jessie Johns is a Clinical Nutritionist that has a deep understanding of how the food we eat impacts our health and wellbeing. She believes that consistently meeting the body’s nutritional requirements with adequate wholefoods is fundamental in not only restoring good health, but to truly heal the body and thrive.
To learn more about Jessie and her offerings, click here